Tennis elbow can make even the simplest daily tasks, like lifting a cup or typing, unexpectedly painful and frustrating. Fortunately, a range of medical devices is available to provide targeted relief, support healing, and restore arm function. This comprehensive guide explores the best devices designed to ease discomfort, improve mobility, and help you get back to your routine with confidence.
Understanding Tennis Elbow and How Medical Devices Help
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, isn’t just for tennis players-it can strike anyone who overuses their forearm, from athletes to desk workers. That nagging pain when you lift your coffee mug, shake hands, or type for hours can be frustrating. Luckily, the right medical devices can ease that discomfort, ease strain, boost circulation, and speed up healing, making everyday movements feel a lot easier.

Common Symptoms of Tennis Elbow
- Pain or a burning sensation on the outer elbow: You might notice a nagging ache or sharp burn where your forearm muscles meet the elbow, especially after repeated movements.
- Weak grip strength: Tasks like holding a coffee cup, opening jars, or shaking hands can suddenly feel frustratingly difficult.
- Pain when lifting or bending your arm: Simple actions like picking up objects or bending your elbow may trigger sharp or dull discomfort.
- Discomfort when twisting your forearm: Everyday motions-turning a doorknob or using a screwdriver, intensify the pain.
-
Pain radiating down the forearm: The ache can spread from your elbow toward your wrist, making even light activities uncomfortable and limiting movement.
How Medical Devices Aid Recovery
- Reducing strain on injured tendons: Braces and supports help take pressure off the affected tendons, allowing them to rest and heal more effectively.
- Providing compression to improve blood flow: Compression sleeves or straps enhance circulation, which can reduce swelling and promote faster recovery.
- Limiting painful movements: Devices can restrict motions that aggravate the injury, preventing further damage while still allowing safe activity.
- Delivering therapeutic modalities (heat, cold, electrical stimulation): Many devices incorporate treatments like heat packs, cold therapy, or TENS units to relieve pain and encourage tissue repair.
- Supporting proper alignment during healing: Splints and ergonomic supports help keep the forearm and elbow in the correct position, ensuring tendons and muscles heal without strain.
Essential Tennis Elbow Medical Devices for Effective Relief
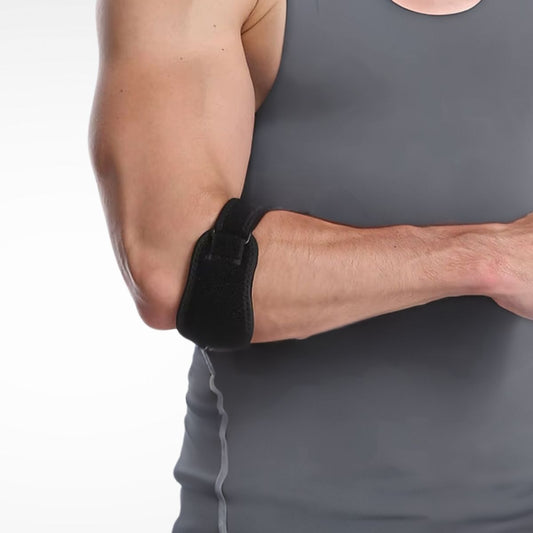
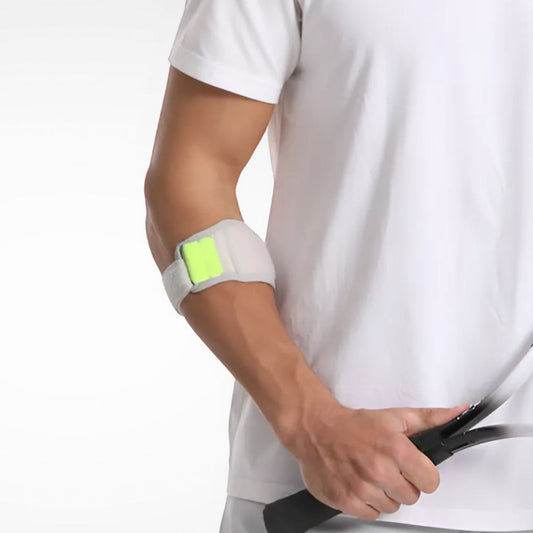
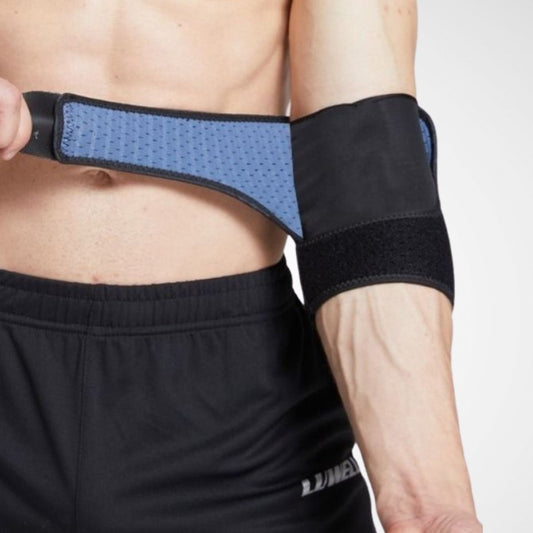
Tennis Elbow Braces and Counterforce Straps
These are narrow straps worn just below the elbow joint to take pressure off the tendon attachment site. They apply targeted pressure to redistribute forces away from the injured area.
Pros:
- Targeted pain relief during activity
- Small and adjustable
- Commonly recommended by orthopaedic specialists
Cons:
- May feel restrictive at first
- Needs proper positioning for best results
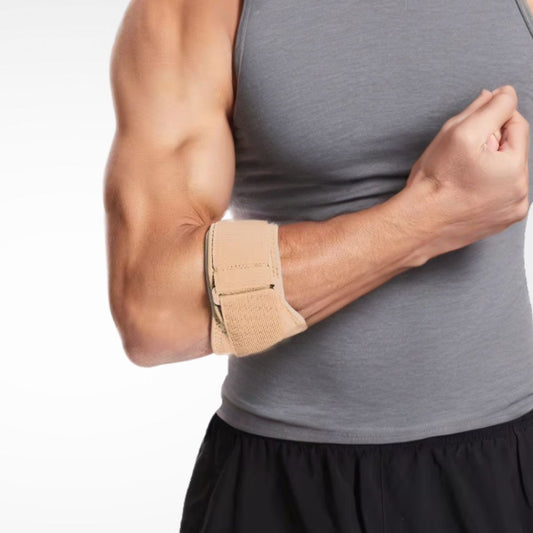
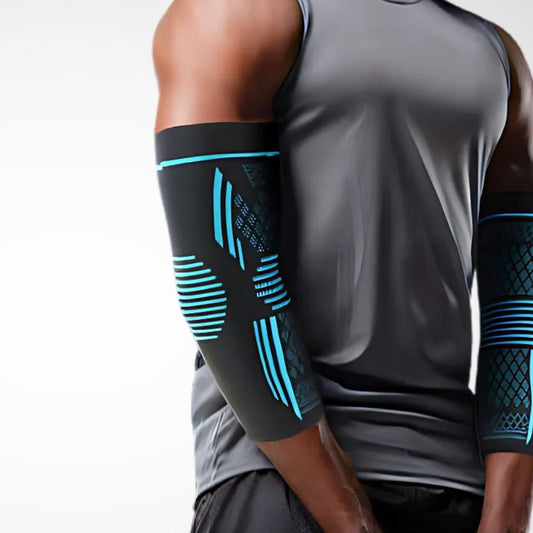
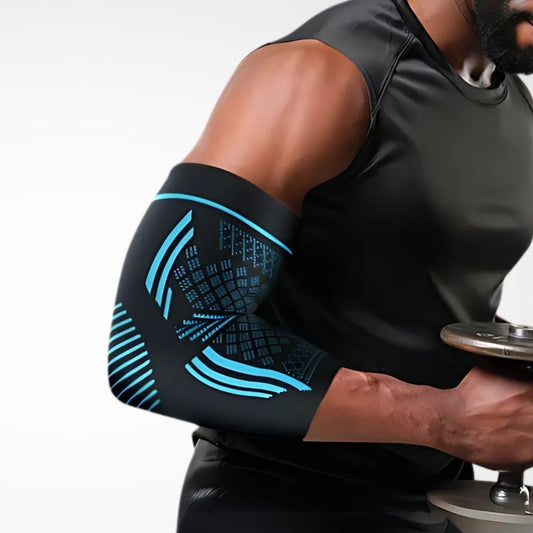
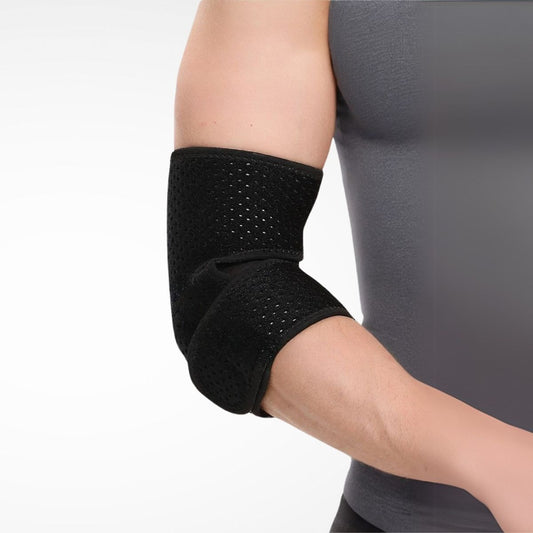
Compression Sleeves and Supports

Full-coverage sleeves provide mild-to-moderate compression to stabilise the elbow and improve circulation. They’re lightweight enough for everyday wear.
Pros:
- Comfortable for extended use
- Promotes blood flow
- Helps manage mild swelling
Cons:
- Less targeted than straps
- May feel warm in hot weather
Hot and Cold Therapy Devices

- Cold Therapy Benefits: Cold packs or gel sleeves reduce inflammation, numb sharp pain, and help after overuse or sports activity.
- Heat Therapy Benefits: Heat wraps improve blood flow, relax tight muscles, and help during later recovery stages.
Pros:
- Non-invasive pain relief
- Easy to use at home
- Drug-free option
Cons:
- Temporary relief only
- Needs repeated application
TENS and EMS Units

TENS and EMS devices are both popular tools for managing tennis elbow, but they serve different purposes. While both use electrical currents, their goals, targets, and benefits aren’t quite the same. Knowing the difference can help you choose the right device for your recovery.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
This device works by sending gentle electrical pulses through the skin to the nerves, which helps block pain signals from reaching the brain. It can also trigger the release of endorphins, your body’s natural painkillers.
EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation)
EMS stimulates muscle contractions, improving blood circulation and preventing the muscles from weakening due to inactivity. It’s especially useful for maintaining strength and flexibility during the healing process.
Pros:
- Can be effective for chronic pain
- Adjustable intensity
- Portable options available
Cons:
- Works best with guidance from a healthcare provider
- Not suitable for everyone (e.g., pacemaker users)
Therapeutic Exercise Tools
|
Exercise Tool |
Primary Function |
Benefits |
|
Resistance Bands |
Strengthening |
Builds forearm and grip strength |
|
Hand Grippers |
Grip training |
Improves daily grip function |
|
Flex Bars |
Eccentric exercise |
Supports tendon healing |
|
Massage Balls/Rollers |
Myofascial release |
Reduces muscle tension and improves mobility |
Ultrasound Therapy Devices
These use sound waves to stimulate deep tissue healing, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility. Often used in physical therapy clinics, but portable home units are available.
Pros:
- Can accelerate recovery
- Non-invasive
- Can be combined with other treatments
Cons:
- Requires proper technique
- Higher upfront cost
When to Use Tennis Elbow Braces
- Computer work and typing: Braces can help reduce strain from repetitive small movements and prolonged wrist extension while working at a keyboard or mouse.
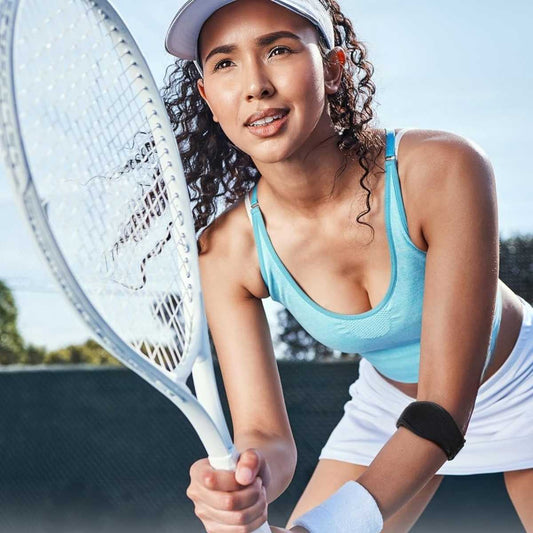
- Racquet sports (tennis, pickleball, badminton): They absorb shock and limit stress on the tendons during repeated swings, helping prevent flare-ups.
- Golf: Supports the forearm muscles during swings, especially when gripping the club tightly or making repetitive strokes.
- Manual labor and construction: Braces provide extra stability when lifting, hammering, or using heavy tools, which often involve repetitive gripping.
- Gardening and household chores: Reduces stress on the elbow when pulling weeds, pruning, scrubbing, or lifting objects around the home.
Ideal Usage Scenarios - Compression
- Recovery periods after activity: Compression supports help reduce post-activity swelling and tendon strain, aiding faster recovery and preventing delayed soreness.
- All-day support for chronic conditions: Wearing compression during the day can stabilise the elbow, reduce pain flare-ups, and provide consistent support for ongoing tendon issues.
- Cold-weather activities when warmth is beneficial: Compression sleeves retain heat, keeping muscles and tendons warm, which improves flexibility and reduces stiffness in colder conditions.
- Use during sleep if comfortable: Gentle compression while sleeping can help maintain proper alignment and support the elbow, promoting overnight recovery.
- Combining with other treatment modalities: Compression works well alongside ice, heat, or TENS/EMS therapy to enhance healing, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain more effectively.
How Ultrasound Therapy Works for Tennis Elbow
- Sound waves penetrate deep into tissues: Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to reach muscles, tendons, and ligaments beneath the skin, targeting the injured area directly.
- Increases local blood flow: The vibrations from the ultrasound stimulate circulation, bringing more oxygen and nutrients to the damaged tissues, which helps speed up healing.
- Reduces inflammation and swelling: Ultrasound energy promotes fluid movement and lymphatic drainage, helping to decrease pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected elbow.
- Stimulates cell repair and tissue regeneration: The therapy encourages collagen production and cellular activity, which supports tendon repair and strengthens the tissue for long-term recovery.
Buying Guide: How to Choose the Right Tennis Elbow Medical Device
Medical Considerations
- Severity of your symptoms: Determines how intensive or frequent treatment should be.
- Any coexisting conditions (arthritis, nerve issues): May affect which devices or therapies are safe to use.
- Recommendations from a healthcare provider: Ensures treatment is tailored and effective for your specific situation.
Product Features
- Adjustable fit: Allows the device to conform comfortably to different arm sizes.
- Breathable materials: Keep the skin cool and reduce sweating during extended use.
- Ease of use: Ensures the device can be applied and removed without difficulty.
- Portability (for travel or work use): Makes it convenient to carry and use anywhere.
Price Considerations for Tennis Elbow Medical Devices
|
Model |
Type |
Price Range |
Best For |
|
Aircast Pneumatic Armband |
Counterforce Strap |
$25–$35 |
Targeted tendon relief |
|
Bauerfeind EpiTrain |
Compression Sleeve |
$80–$100 |
All-day comfort & stability |
|
Therabody Recovery Therm |
Heat/Cold Device |
$150–$200 |
Adjustable temperature therapy |
|
Pure Enrichment PurePulse Pro |
TENS/EMS Unit |
$50–$70 |
Home electrical therapy |
FDA Clearance and Medical Certifications
- Look for products labelled FDA-cleared for orthopaedic use
- Check for medical-grade materials
- Seek devices with ISO or CE certifications for safety and quality
Frequently Asked Questions About Tennis Elbow Medical Devices
1. What is the best device for tennis elbow?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but most people find relief with a well-fitted counterforce strap or compression sleeve.
2. What do doctors recommend for tennis elbow?
Most doctors suggest a combination of rest, physical therapy, and supportive devices like braces or sleeves.
3. What is the best medicine for tennis elbow?
Over-the-counter NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) may help with pain and inflammation, but they should be used under a doctor’s guidance.